An API gateway is essential part of organizing requests that need to be processed by different microservices.
The API Gateway handles all requests and then invokes the appropriate microservices and potentially aggregates the results; it is responsible for communicating between web protocols and the protocols being used by the various applications. For example, AWS’ API Gateway can handle converting requests from text into JSON.
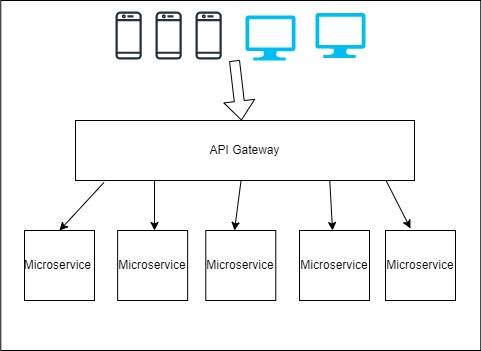
API Gateway is a service that allows us to allow entry into our application from the outside world. The API Gateway is the single-entry point for our defined backend APIs and the microservices whether they are internal or external. It’s primary job is to protect, enforce security, and ensure scalability.




Pingback: What are REST API's constraints? - Brian Cline
Pingback: 5 Tips for Better Caching in a REST API - Brian Cline
Pingback: What are Microservices? - Brian Cline
Pingback: How to find API gateway URLs - Brian Cline